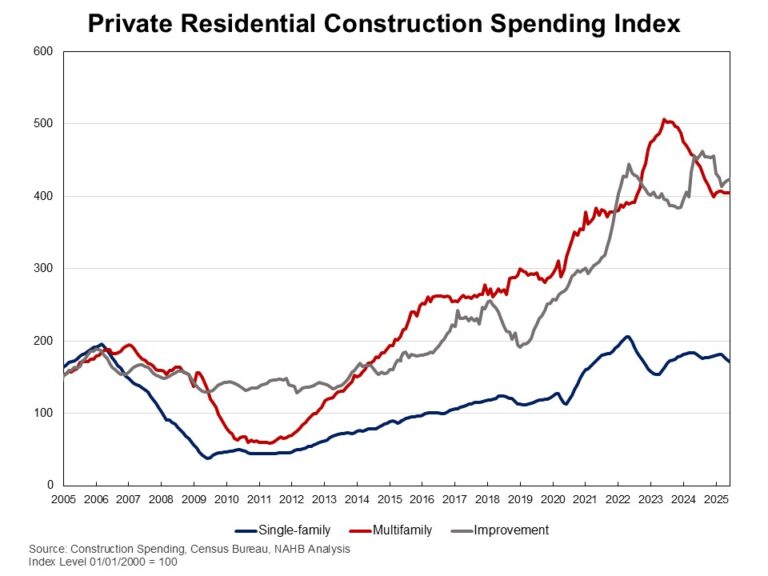
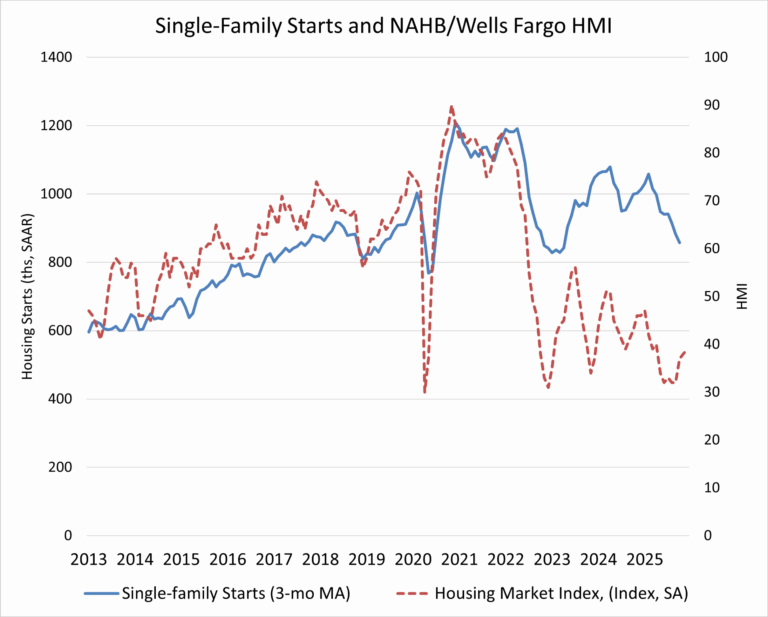The latest residential housing market report, delayed by the federal government shutdown last fall, indicates that builders have faced significant headwinds in recent months. Elevated mortgage rates earlier in the year have restrained buyer demand and weighed on home building activity, alongside persistently high construction costs.
Overall housing starts declined 4.6 percent in October to a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 1.25 million units, according to the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development and the U.S. Census Bureau. This pace reflects the number of housing units builders would begin over the next 12 months if October’s activity were sustained.
Within the total, single-family starts rose 5.4 percent to a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 874,000 units but remain 7.8 percent lower than a year earlier. On a year-to-date basis, single-family starts are down 7.0 percent. Given recent volatility, the three-month moving average provides a clearer signal, declining to 857,000 units.
In contrast, multifamily starts, which include apartment buildings and condominiums, fell sharply, down 22.0 percent to an annualized pace of 372,000 units. The three-month moving average for multifamily construction has trended lower to 424,000 units, and activity is 7.9 percent below year-ago levels.
Regionally and on a year-to-date basis, combined single-family and multifamily starts increased 9.1 percent in the Midwest and 8.5 percent in the Northeast, while declining 1.9 percent in the West and 4.1 percent in the South.
The total number of housing units under construction stood at 1.3 million in October, down 10.1 percent from a year earlier. Single-family homes under construction fell to 596,000 units, a 7.0 percent year-over-year decline and the lowest level since November 2020. Multifamily units under construction declined to 790,000, down from peaks above 1 million units in December 2023 and 4.0 percent lower than a year ago.
Completions of single-family homes remained relatively strong at an annual rate of about 1 million units, reflecting continued progress in finishing projects already underway and marking a 2.0 percent increase from a year earlier. Multifamily completions, however, dropped sharply, down 41.7 percent year over year to a 377,000-unit pace. On a year-to-date basis, total completions across both sectors are down 9.2 percent.
Overall building permits edged down 0.2 percent in October to a 1.41-million-unit annualized rate. Single-family permits declined 0.5 percent to 876,000 units and are 9.4 percent lower than a year ago, with year-to-date permits down 7.0 percent. Multifamily permits were essentially unchanged at a 536,000-unit pace compared to the previous month and are up 16.3 percent compared to October 2024. Regionally, year-to-date total permits increased 5.9 percent in the Midwest, while declining 3.3 percent in the West, 4.0 percent in the South, and 9.3 percent in the Northeast.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .