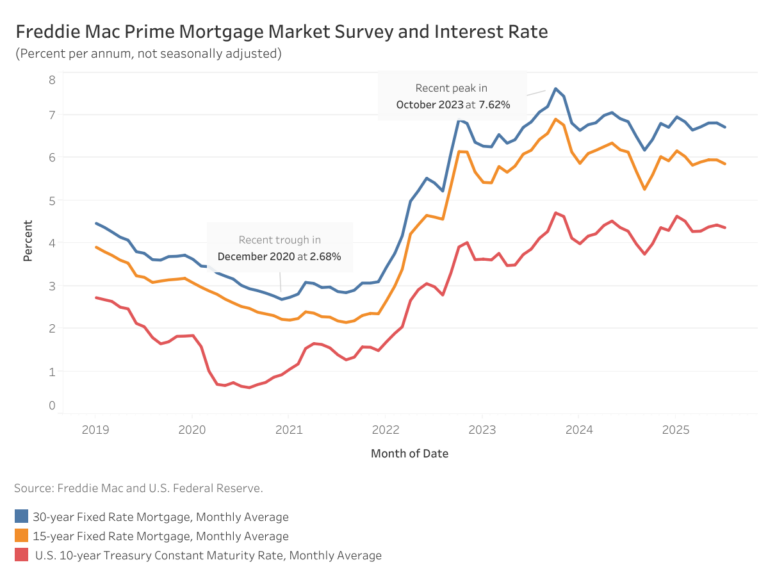
Average mortgage rates dipped in July, according to Freddie Mac. The average 30-year fixed-rate mortgage was 6.72%, 10 basis points (bps) lower than June. Meanwhile, the 15-year rate declined 9 bps to average at 5.86%. Compared to a year ago, the 30-year rate is down 13 basis points (bps), and the 15-year rate is 28 bps lower.
The 10-year Treasury yield, a key benchmark for long-term borrowing, averaged 4.37% in July – a 6 bps decline from the previous month. Yields began the month lower but reversed course and rose steadily as investor expectations solidified that the Federal Reserve would maintain its current policy stance. These expectations were driven by economic data showing an uptick in inflation while the economy and labor market remained solid.
On July 30, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) solidified market expectations by voting to keep the federal funds rate unchanged at 4.25% to 4.50%. However, just days later, the July employment report released by the Bureau of Labor Statistics on Friday, August 1, showed downward revisions to job gains in May and June. In response, yields fell to around 4.2% as investors perceived an increased likelihood of a rate cut at the Fed’s next meeting in September.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .