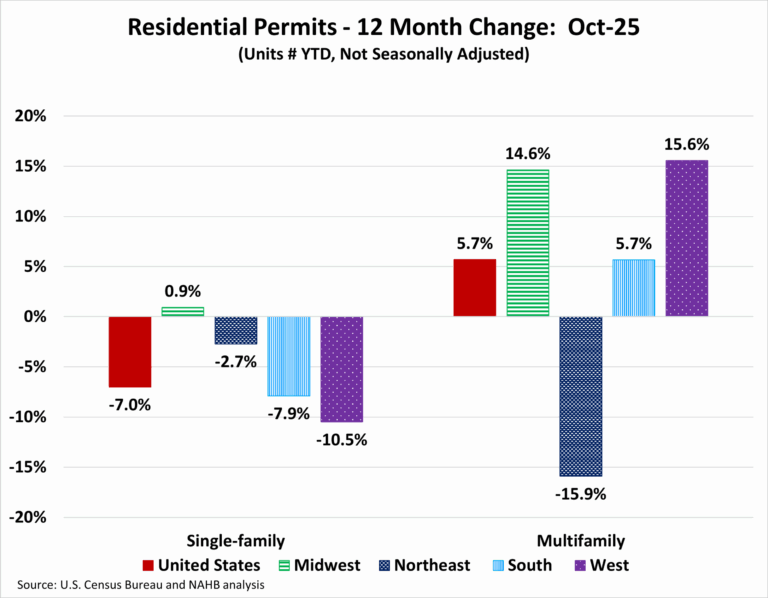
In October, single-family building permits weakened, reflecting continued caution among builders amid affordability constraints and financing challenges. In contrast, multifamily permit activity remained steady and continued to perform relatively well. Together, these trends suggest that while demand for new housing persists, builders are adjusting residential construction activity in response to evolving market conditions. Because permits typically precede construction starts, these patterns offer insight into the near-term outlook for residential building activity.
Over the first ten months of 2025, the number of single-family permits issued nationwide reached 787,122. On a year-over-year basis, this represents a 7.0 percent decline compared with the October 2024 year-to-date total of 846,446. Multifamily permitting activity was stronger, with 426,352 permits issued nationwide, marking a 5.7 percent increase from the same period last year.
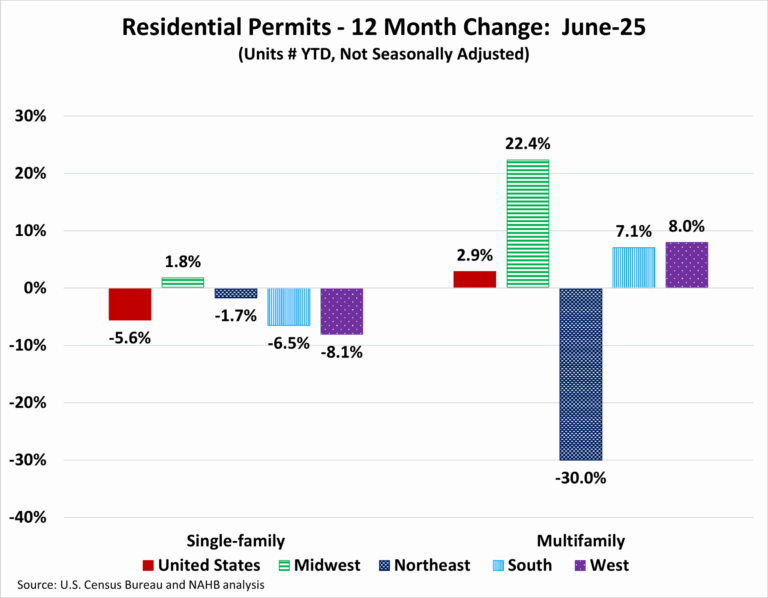
Regionally, year-to-date single-family permitting increased in only one of the four regions through October. The Midwest posted a modest gain of 0.9 percent, while activity declined in the Northeast (down 2.7 percent), the South (down 7.9 percent), and the West (down 10.5 percent). Multifamily permits increased in three of the four regions, led by gains in the West (up 15.6 percent), followed by the Midwest (up 14.6 percent), and then the South (up 5.7 percent). The Northeast saw a sharp decline of 15.9 percent, driven largely by a 28.0 percent drop in the New York–Newark–Jersey City metropolitan area.
At the state level, 15 states recorded year-over-year increases in single-family permits between October 2025 year-to-date and October 2024 year-to-date, with gains ranging from 12.6 percent in New Hampshire to 0.8 percent in West Virginia. The remaining 35 states and the District of Columbia reported declines, led by Nevada, which posted the steepest drop at 22.4 percent.
The ten states issuing the highest number of single-family permits accounted for 62.0 percent of all single-family permits issued nationwide. Texas continued to lead the country, with 122,293 permits issued over the first ten months of 2025, although this represented a 10.3 percent decline compared with the same period last year. Florida, the second-highest state, saw permits fall by 9.8 percent, while North Carolina, ranked third, experienced a decline of 5.8 percent.
Between October 2025 year-to-date and October 2024 year-to-date, 29 states and the District of Columbia recorded increases in multifamily building permits, while 21 states experienced declines. Mississippi posted the largest percentage increase, with multifamily permits surging 142.6 percent, rising from 289 to 701 units. In contrast, Maryland recorded the steepest decline, with permits falling 44.5 percent, from 5,265 to 2,922 units.
The ten states issuing the highest number of multifamily permits accounted for 60.2 percent of all multifamily permits issued nationwide. Over the first ten months of 2025, Texas, which issued the most multifamily permits, recorded a modest increase of 2.9 percent. Florida, the second-highest state, posted a stronger gain of 27.8 percent, while California, ranking third, saw multifamily permits rise by 19.8 percent.
At the local level, the following are the ten metropolitan areas with the highest number of single-family permits issued.
Below are the ten local areas with the highest levels of multifamily permitting activity.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .