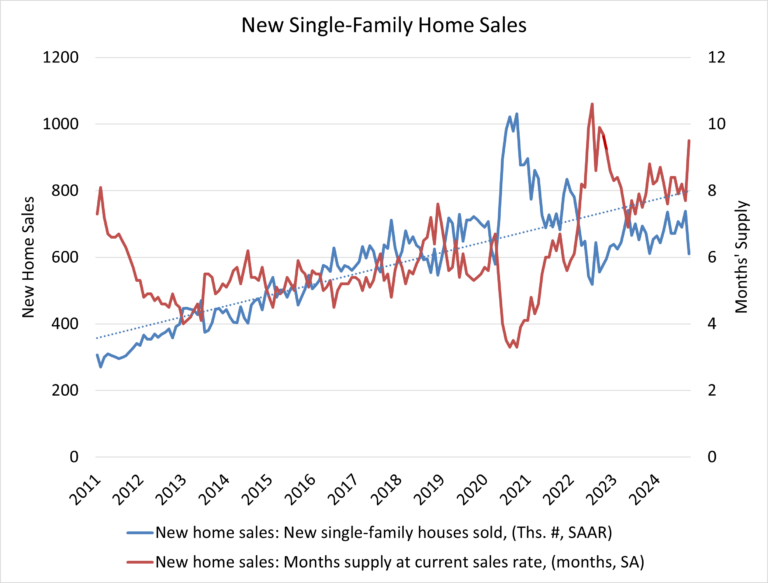
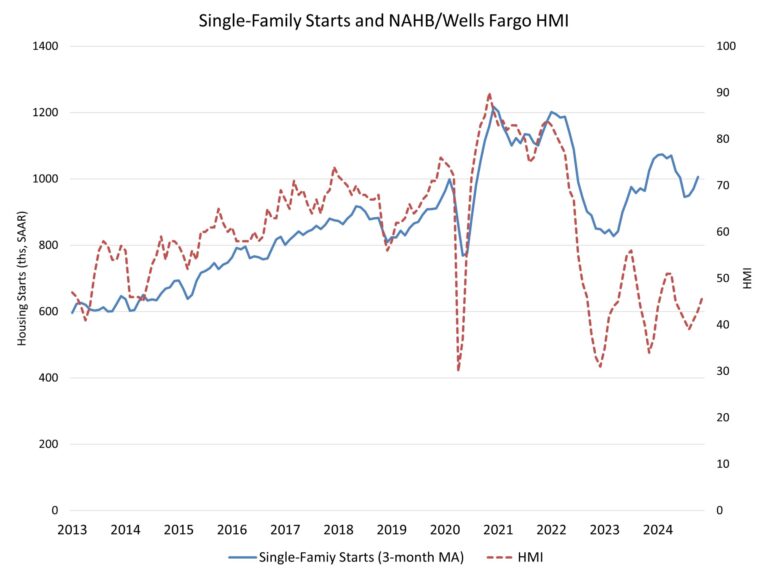
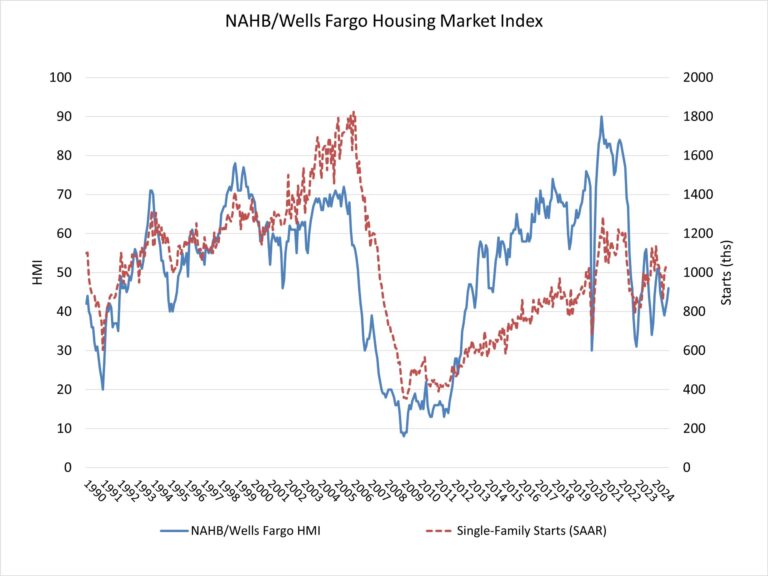
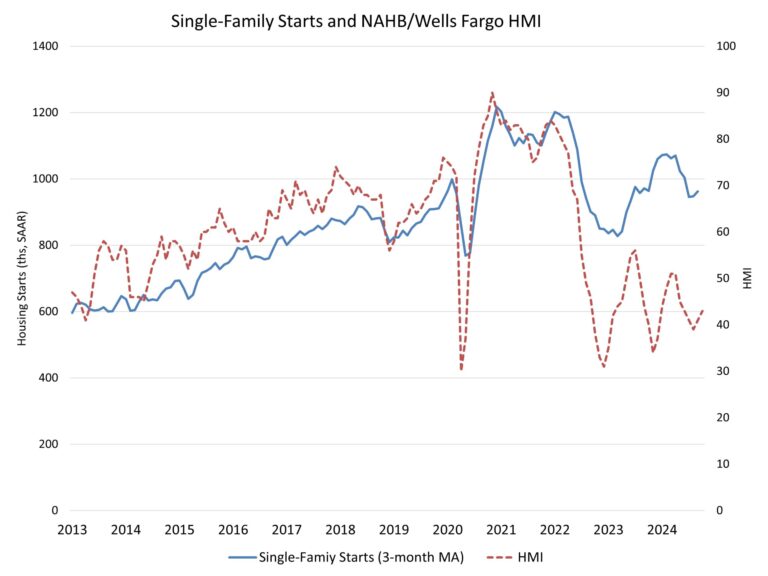
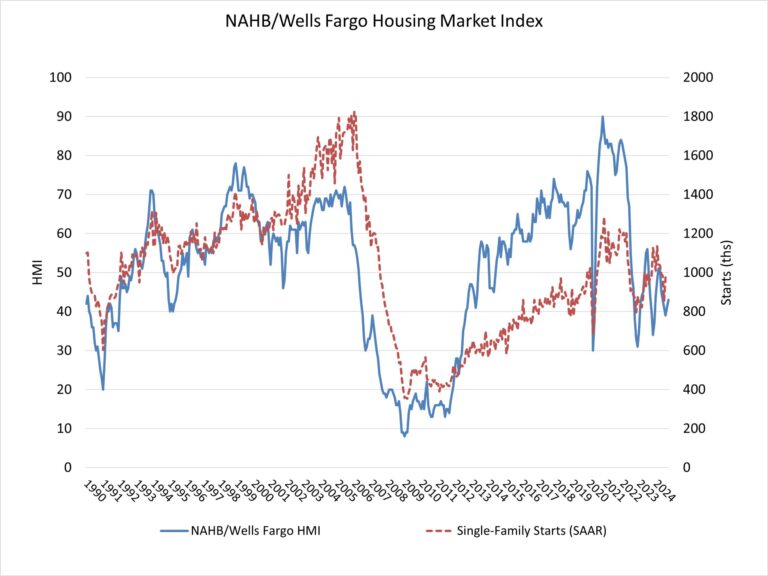
Steadily rising mortgage rates coupled with ongoing affordability challenges kept many potential home buyers on the sidelines in October. Sales of newly built, single-family homes in October declined 17.3% to a 610,000 seasonally adjusted annual rate, according to newly released data from the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development and the U.S. Census Bureau. The pace of new home sales in October is down 9.4% compared to a year earlier. October new home sales are up 2.1% on a year-to-date basis.
A new home sale occurs when a sales contract is signed, or a deposit is accepted. The home can be in any stage of construction: not yet started, under construction or completed. In addition to adjusting for seasonal effects, the October reading of 610,000 units is the number of homes that would sell if this pace continued for the next 12 months.
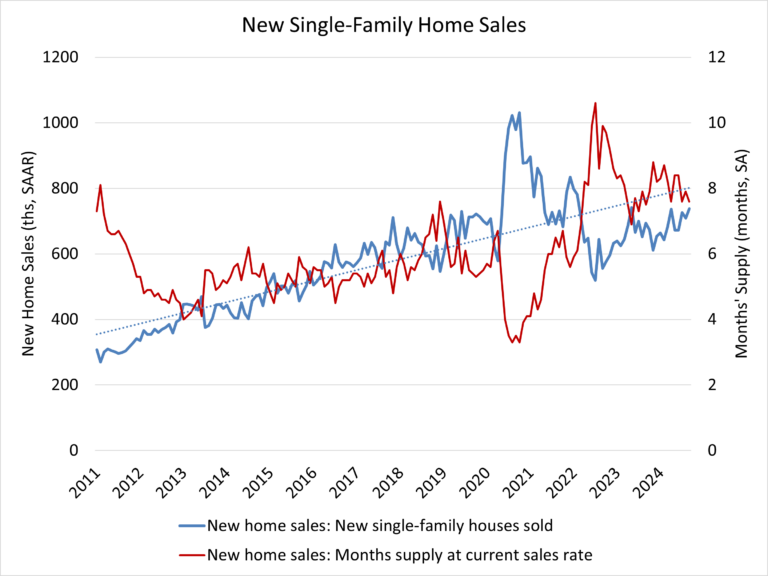
New single-family home inventory in October remained elevated at a level of 481,000, up 8.8% compared to a year earlier. This represents a 9.5 months’ supply at the current sales pace. A measure near a six months’ supply is considered balanced.
While a 9.5 months’ supply may be considered elevated in normal market conditions, there is currently only a 4.2 months’ supply of existing single-family homes on the market. Combined, new and existing total months’ supply remains below historic norms at approximately 4.9 months, although this measure is expected to increase as more home sellers test the market in the months ahead.
A year ago, there were 76,000 completed, ready-to-occupy homes available for sale (not seasonally adjusted). By the end of October 2024, that number increased 52.6% to 116,000. However, completed, ready-to-occupy inventory remains just 24% of total inventory, while homes under construction account for 55% of the inventory. The remaining 22% of new homes sold in October were homes that had not started construction when the sales contract was signed.
The median new home sale price in October edged up 2.5% to $437,300 and is up 4.7% from a year ago. In terms of affordability, the share of entry-level homes priced below $300,000 has been steadily falling in recent years. Only 13% of the homes were priced in this entry-level affordable range, while 37% of the homes were priced above $500,000. Most of the homes were priced between $300,000-$500,000.
Regionally, on a year-over-year basis, new home sales are up 35.3% in the Northeast and 15.9% in the Midwest. New home sales are down 19.7% in the South and 1.3% in the West.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .