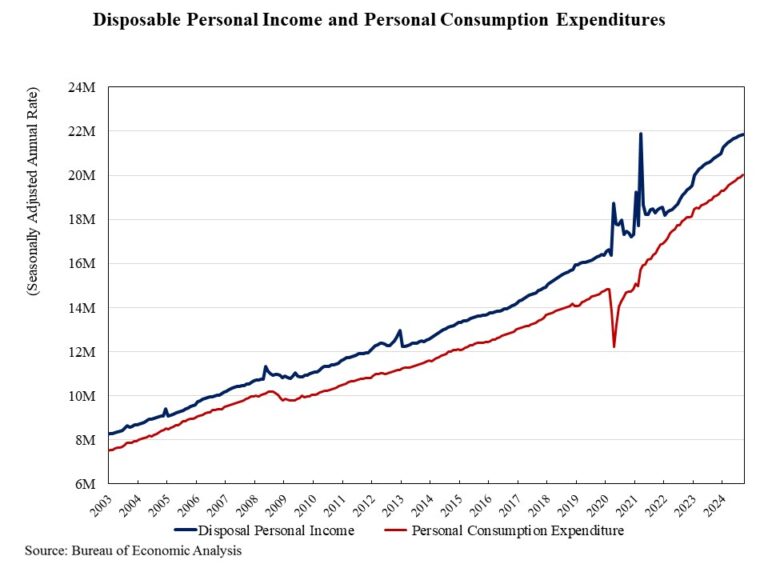
In September 2025, nonfarm payroll employment was largely unchanged across states on a monthly basis, with a limited number of states seeing statistically significant increases or decreases. This reflects generally stable job counts across states despite broader labor market fluctuations. The data were impacted by collection delays due to the federal government shutdown.
Nonfarm payroll employment increased in 29 states and the District of Columbia in September compared to the previous month, while decreasing in 20 states. New Mexico reported no change. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, nationwide total nonfarm payroll employment increased by 119,000 in September, following significant downward revisions to the previous two months’ figures including job losses in August. Through September, monthly job growth has averaged 76,000, a significant slowdown compared to the 168,000 monthly average gain for 2024.
On a month-over-month basis, employment data was most favorable in Missouri, which added 18,300 jobs. New Jersey came in second (+10,900), followed by North Carolina (+10,200). Meanwhile, a total of 96,300 jobs were lost across 20 states, with New York reporting the steepest job losses at 27,000. In percentage terms, employment increased the highest in Missouri at 0.6%, while Connecticut saw the largest decline at 0.3% between August and September.
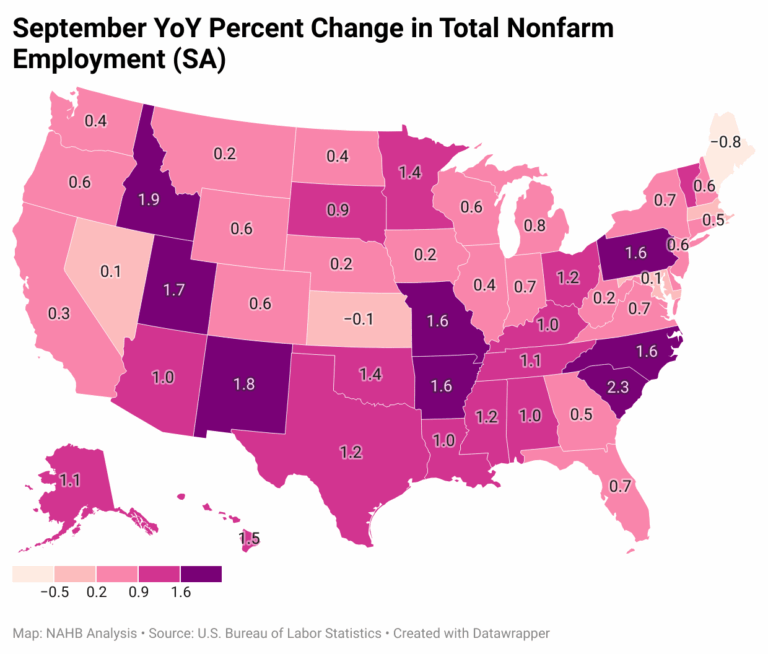
Year-over-year ending in September, 1.3 million jobs have been added to the labor market, which is a 0.8% increase compared to the September 2024 level. The range of job gains spanned from 900 jobs in Montana to 168,000 jobs in Texas. Three states and the District of Columbia lost a total of 25,700 jobs in the past 12 months, with the District of Columbia reporting the steepest job losses at 9,600. In percentage terms, the range of job growth spanned 0.1% in Nevada and Maryland to 2.3% in South Carolina. The range of job losses in Kansas, Massachusetts, Maine, and the District of Columbia spanned 0.1%-1.2%.
Construction Employment
Across the nation, construction sector jobs data —which includes both residential and non-residential construction—showed that 31 states and the District of Columbia reported an increase in September compared to August, while 17 states lost construction sector jobs. The two remaining states reported no change on a month-over-month basis. Texas, with the highest increase, added 4,300 construction jobs, while Florida, on the other end of the spectrum, lost 4,400 jobs. Overall, the construction industry added a net 19,000 jobs in September compared to the previous month. In percentage terms, Michigan reported the highest increase at 2.1%, while Mississippi reported the largest decline at 4.9%.
Year-over-year, construction sector jobs in the U.S. increased by 38,000, which is a 0.5% increase compared to the September 2024 level. Texas added 16,400 jobs, which was the largest gain of any state, while New York lost 16,900 construction sector jobs. In percentage terms, New Mexico had the highest annual growth rate in the construction sector at 12.4%. During this period, New Jersey reported the largest decline of 6.0%.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .