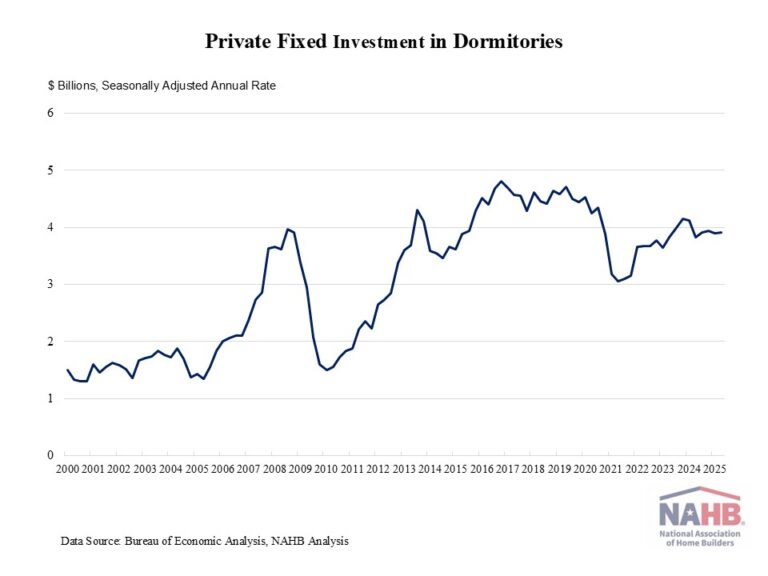
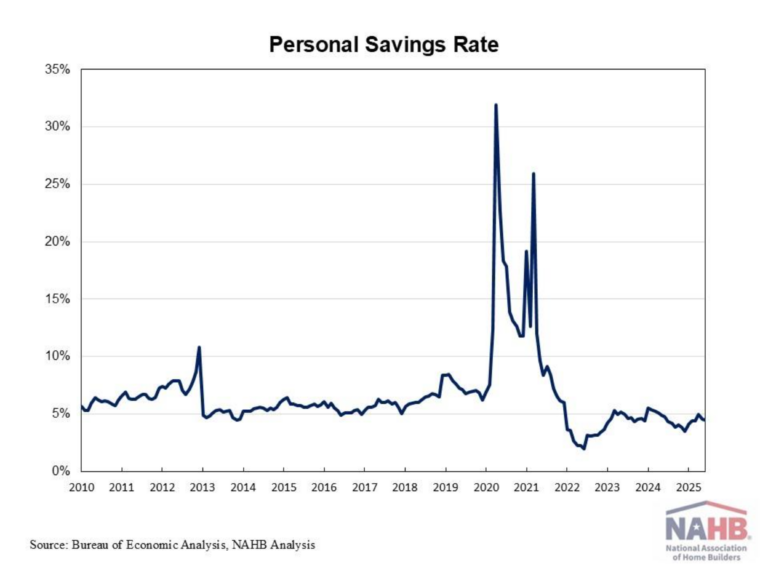
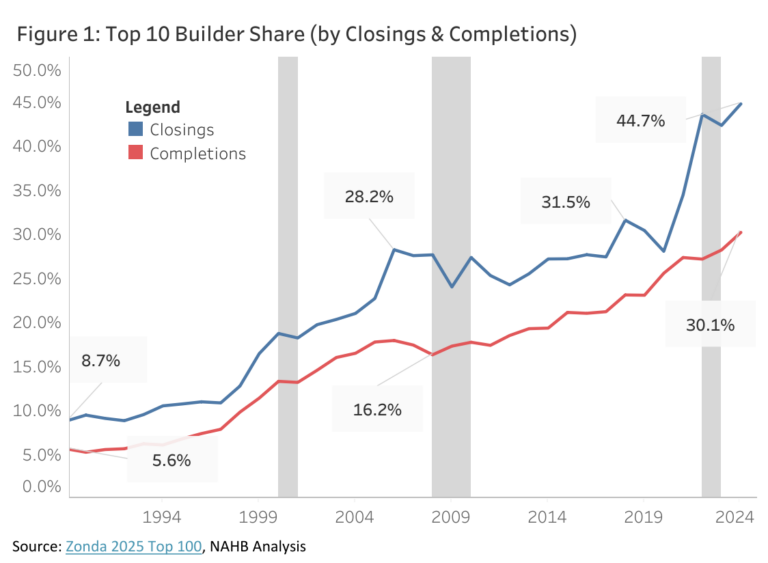
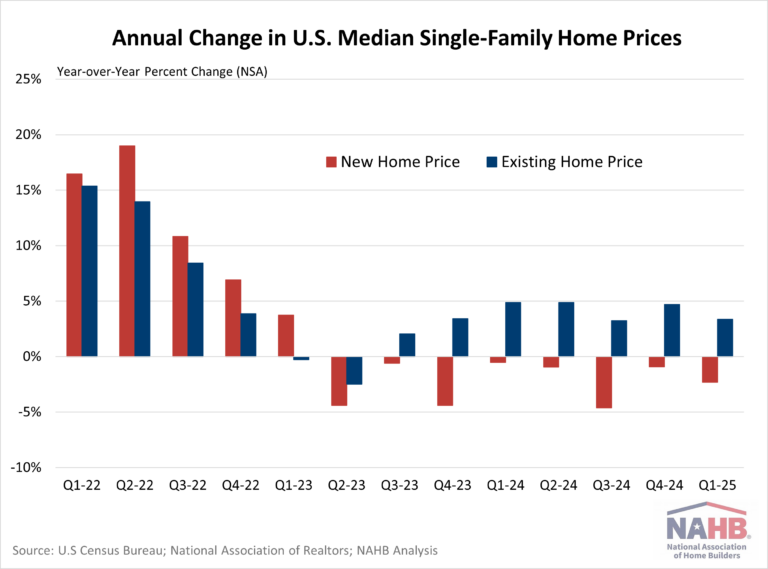
Single-family construction lending picked up in the third quarter, amidst the overall cooling lending environment. Loan balances for 1-4 family construction grew to $91.2 billion in the third quarter, registering the first annual increase in over two years. However, across all acquisition, development and construction (AD&C) loans, the total volume fell for the seventh straight quarter.
According to data from the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), the total level of outstanding AD&C loans fell to $463.0 billion in the third quarter of 2025, down 5.6% from one year ago. This year-over-year decrease was led by a drop in other real estate development loans, which decreased 7% over the year to $371.8 billion. Meanwhile, the volume of 1-4 family residential construction and land development loans rose to $91.2 billion in the third quarter, up 0.5% from one year ago.
It is worth noting, the FDIC data represent only the stock of loans, not changes in the underlying flows, so it is an imperfect data source. Nonetheless, lending remains much reduced from years past. The current amount of existing 1-4 family residential AD&C loans now stands 56% lower than the peak level of residential construction lending of $204 billion reached during the first quarter of 2008. Alternative sources of financing, including equity partners, have supplemented this capital market in recent years.
Quality Metrics of Construction Loans
While the total volume of 1-4 family residential construction loans rose, the volume of loans 30+ days past due or nonaccrual status fell slightly to $1.1 billion over the quarter. As a share of the total 1-4 family residential construction loan volume, this accounts for 1.2%.
Breaking this out further, the level of loans 30-89 days past due was $418.1 million, while the volume in nonaccrual status was $593.4 million. The nonaccrual loan status volume increased from $572.4 million in the second quarter and the 30-89 past due fell from $469.2 million.
Loans are classified as nonaccrual when one or more of the following conditions apply: the loan is 90 days or more past due on principal or interest (unless it is well-secured and in the process of collection); the bank no longer expects full repayment of principal and interest; or the borrower’s financial condition has significantly deteriorated, warranting cash-basis accounting.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .