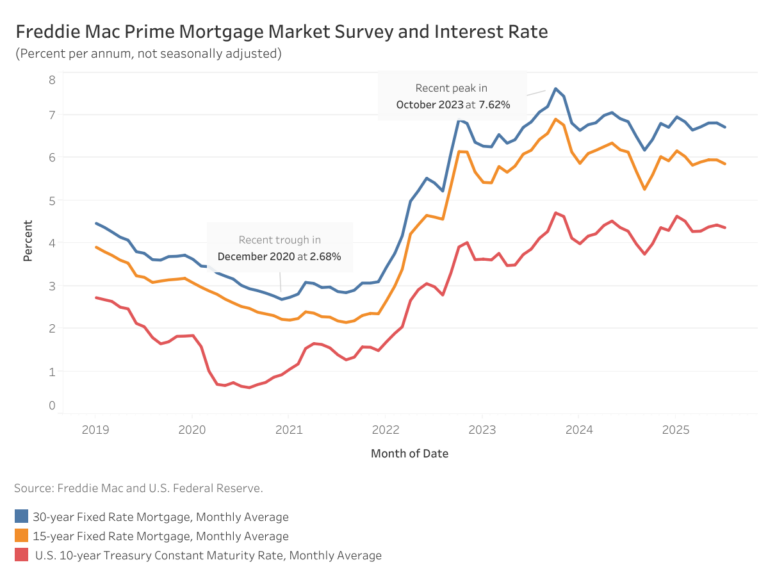
The new home sector has played an increasingly important role in meeting housing demand as resale inventory remains constrained in many regions. The latest data released today (and delayed because of the government shutdown in fall of 2025) indicate that new single-family home sales continue to reflect a stabilizing market after a period of heightened volatility. While month-to-month activity shows some variability, sales remain stronger than a year ago, signaling that buyer interest in newly built homes has improved.
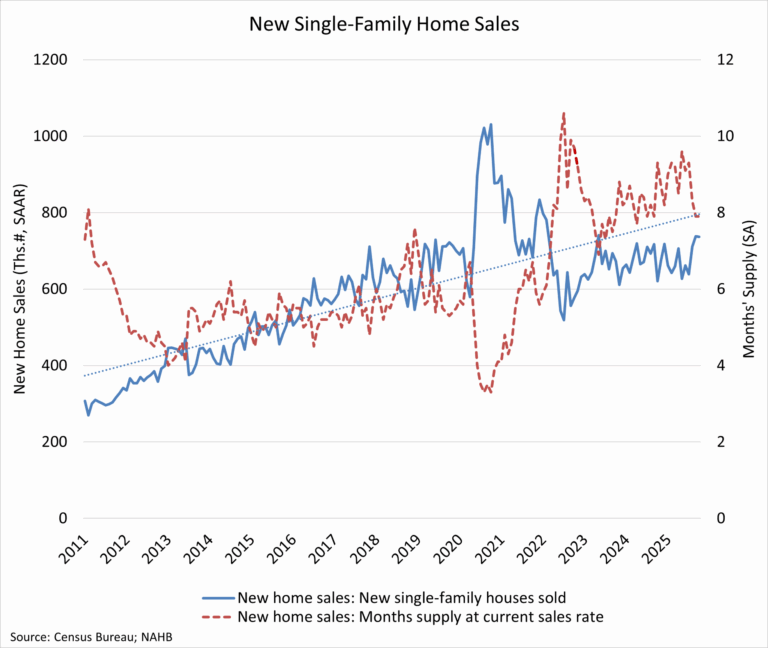
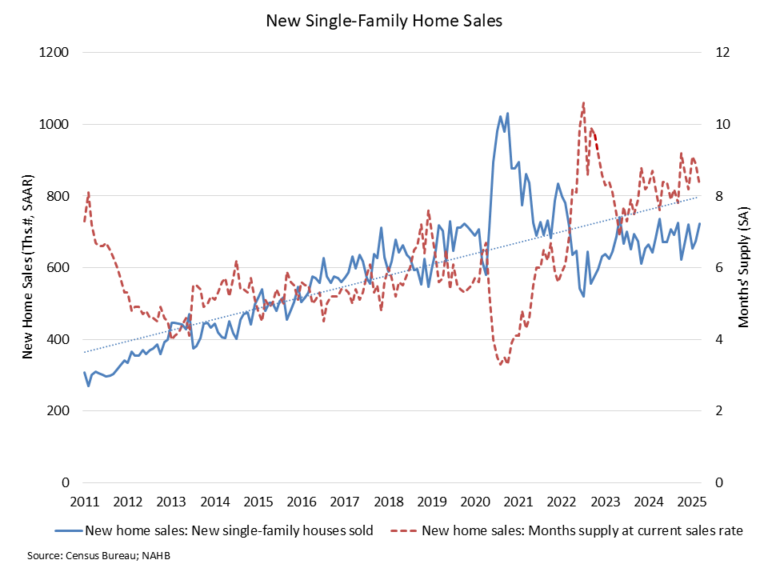
Sales of newly built single-family homes increased 18.7 percent year over year in October to a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 737,000 units, according to the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development and the U.S. Census Bureau. This represented a modest 0.1 percent decline from September and a 1.2 percent decrease on a year-to-date basis. A new home sale is recorded when a contract is signed or a deposit is accepted, regardless of the stage of construction. The seasonally adjusted annual rate reflects the pace of sales that would occur over a 12-month period if current conditions persisted.
New single-family home inventory totaled 488,000 units in October, unchanged from the prior month and 1.7 percent higher than a year earlier. At the current sales pace, the months’ supply of new homes stood at 7.9, down from 9.3 months one year ago, though still above the six-month level that is generally considered balanced.
Combined new and existing home inventory has edged lower in recent months, with total months’ supply declining to 4.9, reflecting slower construction activity. Meanwhile, inventory conditions in the existing home market have shown gradual improvement, and moderating prices across both markets have helped support buyer demand amid ongoing affordability concerns.
By the end of October 2025, there were 124,000 completed, ready-to-occupy homes available for sale on a not seasonally adjusted basis, up 10.7 percent from a year earlier. Completed homes accounted for roughly one-quarter of total inventory, while homes under construction made up 51 percent. The remaining 24 percent of homes sold in October had not yet started construction at the time the sales contract was signed.
Home prices showed further signs of easing in October. The median new home sale price declined 3.3 percent to $392,300, marking an 8.0 percent decrease from a year ago. Affordability improved at the lower end of the market, with 25 percent of new homes priced below $300,000, the highest share in recent months. Thirty percent of homes were priced above $500,000, while the remaining 45 percent fell within the $300,000 to $500,000 range.
Regionally, year-to-date new home sales declined in three of the four regions, falling 0.1 percent in the Midwest, 7.2 percent in the West, and 22.9 percent in the Northeast. The South was the only region to post growth, with sales up 2.9 percent.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .