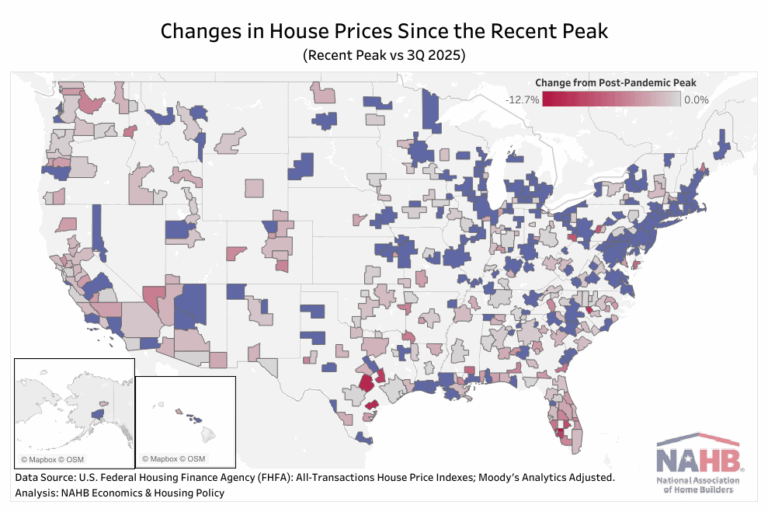
Nationally, house prices continued to rise at a modest pace in the third quarter of 2025, as mentioned in our previous quarterly house prices post. However, this national trend masks significant variation across local markets. While many metro areas continued to see house price appreciation, others experienced notable declines following several years of rapid growth.
Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, house prices have surged nationwide. Between the first quarter of 2020 and the third quarter of 2025, national house prices climbed 54.9%. Local markets saw broad gains as well, with cumulative appreciation ranging from 18.3% to 88.4%, and 159 metro areas reached their highest recorded house prices in the third quarter of 2025.
Yet despite these increases, more than half of metro areas have now experienced at least some decline from their recent price peak. These declines range from a slight 0.1% dip to a more substantial 12.7% decline, with most of the downward trends beginning in last 2024 or early 2025.
House price declines have been most widespread in the West and South, regions that saw some of the fastest appreciation during the pandemic boom. Several markets stand out for their significant corrections:
Punta Gorda, FL has experienced the sharpest decline, with prices falling 12.7% since its peak in the fourth quarter of 2022.
Austin–Round Rock–San Marcos, TX, one of the nation’s hottest markets during the pandemic, has seen prices drop 11.3% since reaching a peak in the second quarter of 2022.
Victoria, TX reached its peak more recently in the fourth quarter of 2024 and has since seen prices decline 11.0% over the past three quarters.
In contrast, many metro areas in the Midwest and Northeast have avoided significant price declines. These regions continue to see slower but steady price growth, supported by persistent inventory shortages and solid demand. Their more moderate appreciation during the pandemic has also helped limit the risk of sharp price corrections. Here are some examples (listed in no particular order):
York–Hanover, PA recorded a 6.0% year-over-year increase in house prices in the third quarter of 2025, reflecting stable demand and limited housing supply.
Worcester, MA continues to experience price growth, slowing from the rapid 18.0% growth in the third quarter of 2021 to a still-solid 4.4% year-over-year gain in the third quarter of 2025.
Wausau, WI experienced a robust 9.5% year-over-year increase in home prices, standing out as one of the strongest and most resilient housing markets in the region.
Milwaukee-Waukesha, WI continue to see rising house prices, with growth easing from a peak of 16.7% growth in the second quarter of 2022 to a more sustainable 5.6% year-over-year increase in the third quarter of 2025.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .