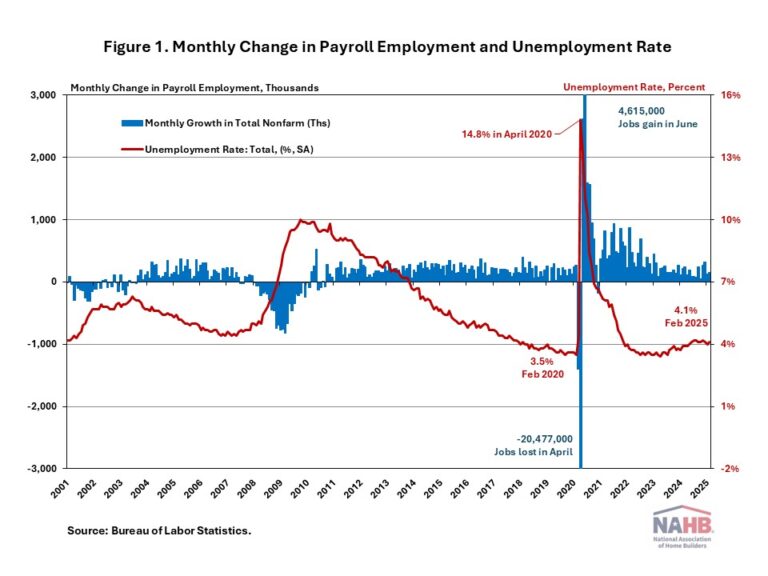
The U.S. job market continued to grow at a solid pace in February, with the unemployment rate edging up slightly to 4.1%. The labor market remains healthy overall, but there are signs of potential weakness in the coming months, driven by mass federal government layoffs and ongoing policy uncertainty.
This month’s jobs report may not fully reflect the impact of these layoffs in both the federal government and private sector, as the reference period for the monthly jobs report only covers the pay period that includes the 12th of the month. In fact, government job losses totaled only 10,000 workers for the February report.
In February, wage growth accelerated. Year-over-year, wages grew at a 4.0% rate, down 0.1 percentage points from a year ago. Wage growth has been outpacing inflation for nearly two years, which typically occurs as productivity increases.
National Employment
According to the Employment Situation Summary reported by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), total nonfarm payroll employment rose by 151,000 in February, following a downwardly revised increase of 125,000 jobs in January. Since January 2021, the U.S. job market has added jobs for 50 consecutive months, making it the third-longest period of employment expansion on record.
The estimates for the previous two months were revised. The monthly change in total nonfarm payroll employment for December was revised up by 16,000 from +307,000 to +323,000, while the change for January was revised down by 18,000 from +143,000 to +125,000. Combined, the revisions were 2,000 lower than previously reported.
The unemployment rate rose to 4.1% in February. While the number of employed persons decreased by 588,000, the number of unemployed persons increased by 203,000.
Meanwhile, the labor force participation rate—the proportion of the population either looking for a job or already holding a job—decreased two percentage points to 62.4%. For people aged between 25 and 54, the participation rate remained unchanged, at 83.5%. While the overall labor force participation rate remains below its pre-pandemic levels of 63.3% at the beginning of 2020, the rate for people aged between 25 and 54 exceeds the pre-pandemic level of 83.1%.
In February, employment rose in several sectors, including health care (+52,000), financial activities (+21,000), transportation and warehousing (+18,000), and social assistance (+11,000). However, within the government sector, federal government employment saw a decline of 10,000, marking the worst month of federal government net hiring since June 2022.
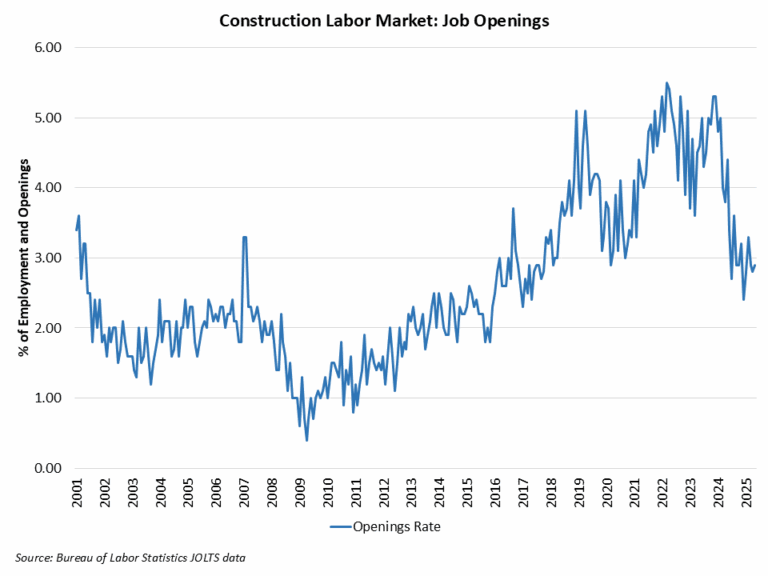
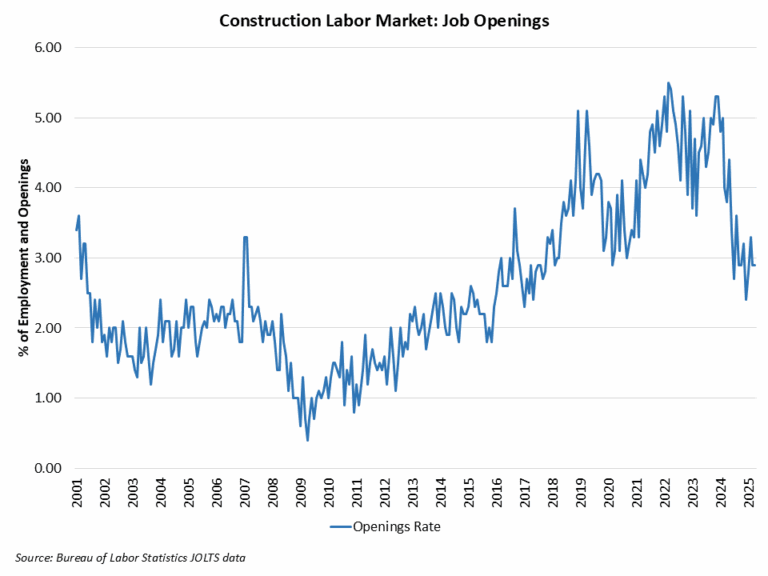
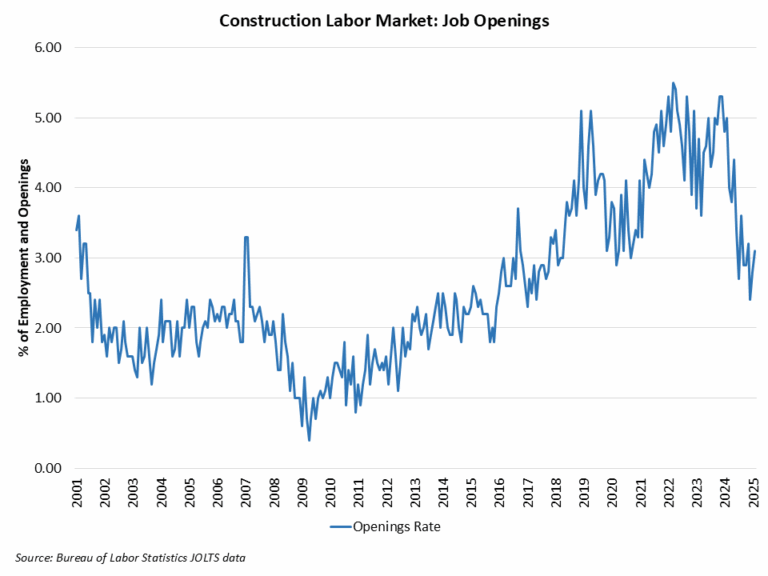
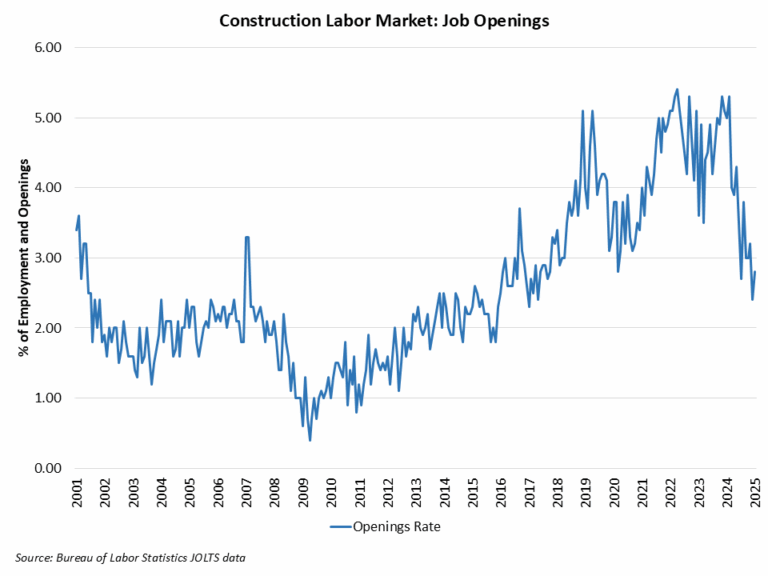
Construction Employment
Employment in the overall construction sector increased by 19,000 in February, after a 2,000 gain in January. While residential construction gained 12,700 jobs, non-residential construction employment added 6,200 jobs for the month.
Residential construction employment now stands at 3.4 million in February, broken down as 955,000 builders and 2.4 million residential specialty trade contractors. The 6-month moving average of job gains for residential construction was 2,600 a month. Over the last 12 months, home builders and remodelers added 50,500 jobs on a net basis. Since the low point following the Great Recession, residential construction has gained 1,387,000 positions.
In February, the unemployment rate for construction workers rose to 5.3% on a seasonally adjusted basis. The unemployment rate for construction workers has remained at a relatively lower level, after reaching 15.3% in April 2020 due to the housing demand impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.