Residential building material prices rose at a slower rate in January, according to the latest Producer Price Index release from the Bureau of Labor Statistics. This was the first decline in the rate of price growth since April of last year. Metal products continue to experience price increases, while specific wood products are showing declines in prices.
The Producer Price Index for final demand increased 0.5% in January, after rising 0.4% in December. The January increase in final demand is linked directly to final demand services, which saw prices rise 0.8% in January. The index for final demand goods decreased 0.3% in January.
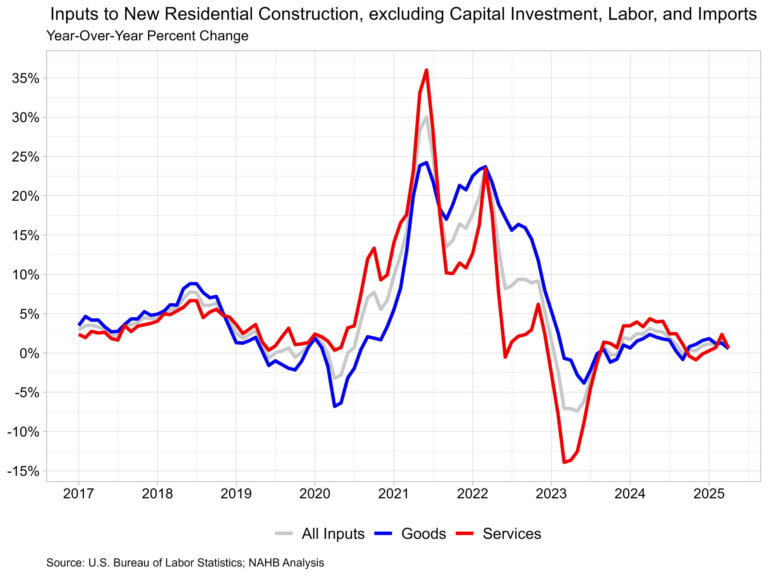
The price index for inputs to new residential construction rose 0.7% in January and was up 3.3% from last year. The price of goods used in new residential construction was up 0.9% over the month and 2.4% from last year. Meanwhile, the price for services was up 0.3% over the month and up 4.7% from last year.
Input Goods
The goods component has a larger importance to the inputs to residential construction price index, representing around 60%. On a monthly basis, the price of input goods to new residential construction was up 0.9% in January.
The input goods to residential construction index can be further broken down into two separate components, one measuring energy inputs with the other measuring remaining goods. The latter of these two components simply represents building materials used in residential construction, which makes up around 93% of the goods index.
Energy input prices fell 0.9% in January and were 10.3% lower than one year ago. Building material prices were up 1.0% in January and up 3.3% compared to one year ago, marking the lowest year-over-year price change since July of last year.
The largest year-over-year price increases continue to show in metal products. Topping the list in January was metal molding and trim, with prices up 48.3% from last year. One product that has seen rapid price growth acceleration over the past few months has been nonferrous metal and cable with prices up 19.7%. Price declines for materials over the year are concentrated among wood products with prices for particleboard and fiberboard down 24.4%, treated wood products down 5.0%, and softwood lumber down 3.3%.
Input Services
Prices for service inputs to residential construction reported an increase of 0.3% in January. On a year-over-year basis, service input prices were up 4.7%. The price index for service inputs to residential construction can be broken out into three separate components: a trade services component, a transportation and warehousing services component, and a services excluding trade, transportation, and warehousing component (other services).
The most significant component is trade services (around 60%), followed by other services (around 29%), and finally transportation and warehousing services (around 11%). The largest component, trade services, was up 7.1% from a year ago. The transportation and warehousing services rose 2.0%, while prices for other services were up 1.1% over the year.
Expanded Inputs to New Construction
Within the PPI that BLS publishes, new experimental data was recently published regarding inputs to new construction. The data expands existing inputs to industry indexes by incorporating import prices with prices for domestically produced goods and services. With this additional data, users can track how industry input costs are changing among domestically produced products and imported products. This data focuses on new construction, but the complete dataset includes indices across numerous industries that can be found here on BLS website.
New construction input prices are primarily influenced by domestically produced goods and services, with domestic products accounting for 90% of the weight of the industry index for new construction. Imported goods make up the remaining 10% of the index.
The latest available data, for November 2025, showed that domestically produced goods continue to have faster price growth compared to imported goods used in new construction. On a year-over-year basis, the index for domestic goods increased 3.0%, while prices for imported goods have fallen 3.0%.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .