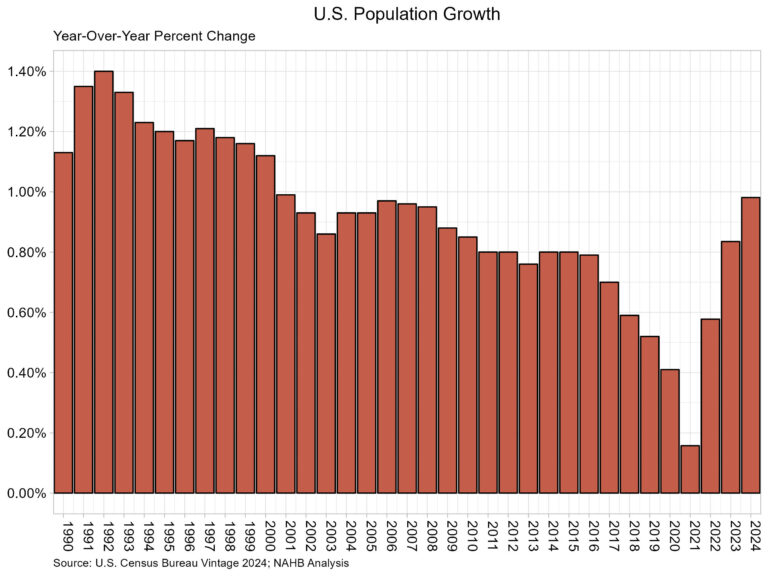
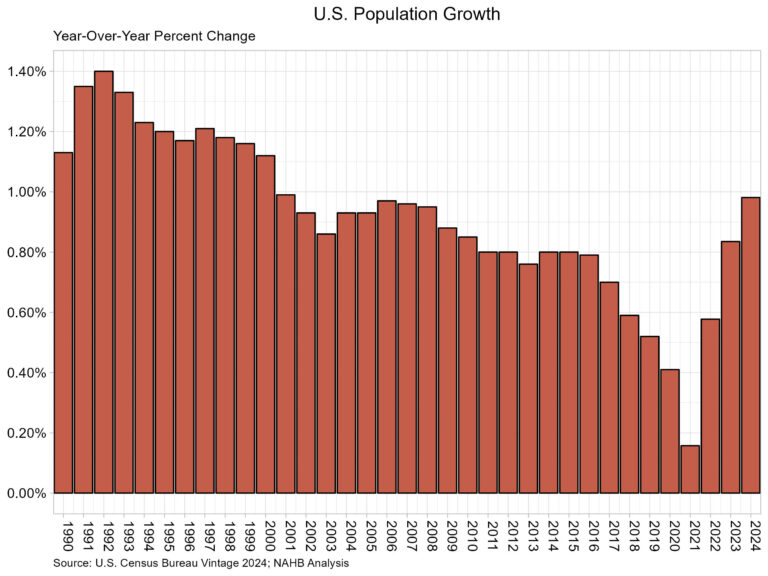
According to the U.S. Census Bureau’s latest estimates, the U.S. resident population grew by 3,304,757 to a total population of 340,110,988. The population grew at a rate of 0.98%, the highest rate since 0.99% in 2001. This also marked the third straight increase in the growth rate of the U.S. population. The vintage population estimates are released annually and represent the change in the U.S. population between July 1st of 2023 and 2024.
The Census Bureau reports that the primary source of population growth was net international migration (immigration), as international migration levels once again were higher than the previous year. The level of net international migration between 2023 and 2024 was 2,786,119. The second component of population growth is natural growth, which represents births minus deaths. Births totaled 3,605,563, down slightly from last year, while the number of deaths was reported at 3,086,925, also a decrease from last year. The natural growth, therefore, between 2023 and 2024 was 518,638.
Each region in the U.S. experienced population growth for the 2023-2024 period. The South led in population growth at 1.34% followed by the West at 0.85%. Meanwhile, the Midwest population grew 0.75%, while the Northeast grew the least at 0.59%.
At the State level, 47 States and the District of Columbia had a population increase over the year. Of note, D.C. had the highest growth rate at 2.13%. Florida was second with population growth at 2.00% followed by Texas at 1.80%. Numerically, Texas experienced the largest population increase gaining 562,941. This was followed by Florida at 467,347 and California at 232,570.
Only three states lost population or remained level according to Census estimates. Vermont and West Virginia tied with a decline of 0.03%. Meanwhile Mississippi saw no population change.
California remained the most populous state by a healthy margin. California’s population was at 39,198,693, while the next most populous state was Texas at 31,290,831. To round out the top five States by total population the proceeding highest were Florida (23,372,215), New York (19,867,248), and Pennsylvania (13,078,751).
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .