A sharp decline in multifamily production pushed overall housing starts down in May, while single-family output was essentially flat due to economic and tariff uncertainty along with elevated interest rates.
Overall housing starts decreased 9.8% in May to a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 1.26 million units, according to a report from the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development and the U.S. Census Bureau.
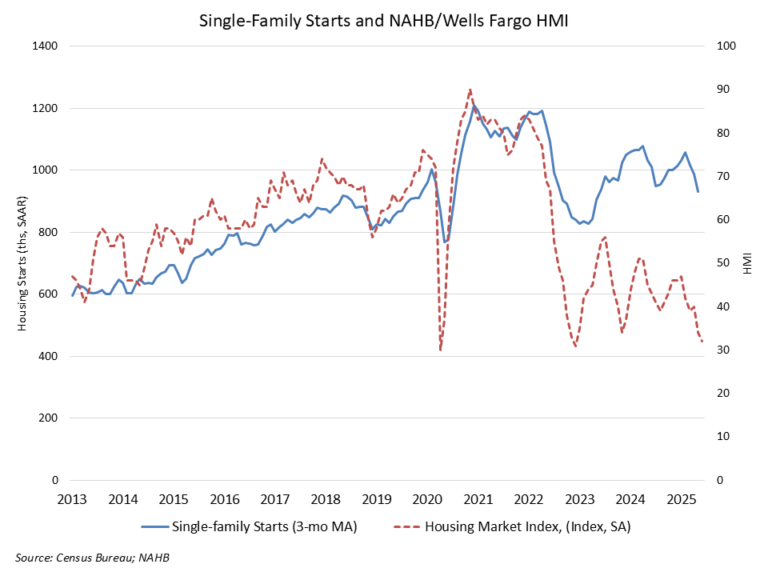
The May reading of 1.26 million starts is the number of housing units builders would begin if development kept this pace for the next 12 months. Within this overall number, single-family starts increased 0.4% to a 924,000 seasonally adjusted annual rate and are down 7.3% compared to May 2024. The volatile multifamily sector, which includes apartment buildings and condos, decreased 29.7% in May to an annualized 332,000 pace.
On a year-to-date basis, single-family starts are down 7.1%. In contrast, multifamily 5-plus unit starts are up 14.5% as more prospective home buyers remain on the sidelines helping rental demand.
Single-family permits and construction starts are down on a year-to-date basis for 2025 for what has been a disappointing spring housing market, given ongoing elevated mortgage interest rates, challenging housing affordability conditions led by higher construction costs, and macroeconomic uncertainty. NAHB is forecasting that 2025 will end with a decline for single-family housing starts.
The number of single-family homes currently under construction totaled 623,000 homes as of May. This is 1.3% lower than April, 7.6% lower than a year ago and 25% lower than the post-Great Recession peak level in June 2022. There were 752,000 apartments under construction in June, 4.6% lower than May and 18.2% lower than a year ago.
On a regional and year-to-date basis, combined single-family and multifamily starts were 21.1% higher in the Northeast, 10.8% higher in the Midwest, 6.8% lower in the South and 1.6% lower in the West.
Overall permits decreased 2% to a 1.39-million-unit annualized rate in May. Single-family permits decreased 2.7% to an 898,000-unit rate and are down 6.4% compared to May 2024. Multifamily permits decreased 0.8% to a 495,000 pace.
Looking at regional permit data on a year-to-date basis, permits were 17.2% lower in the Northeast, 6% higher in the Midwest, 5.4% lower in the South and 3.7% lower in the West.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .