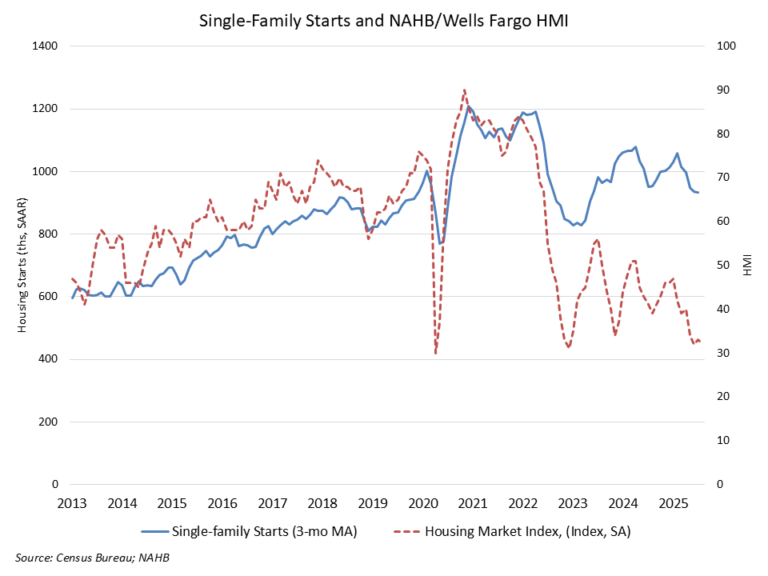
Single-family housing starts posted a modest gain in July as builders continue to contend with challenging housing affordability conditions and a host of supply-side headwinds, including labor shortages, elevated construction costs and inefficient regulatory costs.
Led by solid multifamily production, overall housing starts increased 5.2% in July to a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 1.43 million units, according to a report from the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development and the U.S. Census Bureau.
The July reading of 1.43 million starts is the number of housing units builders would begin if development kept this pace for the next 12 months. Within this overall number, single-family starts increased 2.8% to a 939,000 seasonally adjusted annual rate and are down 4.2% on a year-to-date basis. The multifamily sector, which includes apartment buildings and condos, increased 9.9% to an annualized 489,000 pace.
The slowdown in single-family home building has narrowed the home building pipeline. There are currently 621,000 single-family homes under construction, down 1% in July and 3.7% lower than a year ago. This is the lowest level since early 2021 as builders pull back on supply.
On a regional and year-to-date basis, combined single-family and multifamily starts were 10.2% higher in the Northeast, 17.7% higher in the Midwest, 2.4% lower in the South and 0.5% lower in the West.
Overall permits decreased 2.8% to a 1.35-million-unit annualized rate in July. Single-family permits increased 0.5% to an 870,000-unit rate and are down 5.8% on a year-to-date basis. Multifamily permits decreased 8.2% to a 484,000 pace.
Looking at regional permit data on a year-to-date basis, permits were 16.6% lower in the Northeast, 9.1% higher in the Midwest, 3.4% lower in the South and 5.1% lower in the West.
Discover more from Eye On Housing
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
This article was originally published by a eyeonhousing.org . Read the Original article here. .






Bringing a fresh look to a historical home’s landscape while still maintaining some original charm means navigating a fine line between past and present.
Challenge: Designer Sara Yant of Twistleaf was tasked with reimagining outdoor spaces in the Historic District of Fredericksburg, Texas, including for a Queen Anne Victorian mansion, a carriage house, a five-unit barn conversion and three 1930s bungalows. “We needed to create a cohesive look that would complement the different architectural styles and prioritize an intuitive circulation between the spaces,” Yant says.
There were some hiccups along the way that impacted the original plan. A long-abandoned and crumbling drainage pipe beneath the mansion’s front yard was a safety risk. Stringent watering restrictions also were implemented for the Texas Hill Country during that time.
Solution: Yant replaced the fencing and gates with period-appropriate designs. She also updated the hardscape using a mix of concrete, bricks and decomposed granite to create paths and relaxing courtyards and retreats. Removing the crumbling pipe allowed her to reinforce the surrounding ground.
She finished the space with a mix of native and adapted plants that complement the architecture of the Queen Anne Victorian home. Black and blue sage and soft leaf yucca provide seasonal interest and attract butterflies and hummingbirds. American beautyberries (Callicarpa americana, USDA zones 6 to 10; find your zone), dwarf palmetto palms (Sabal minor, zones 7 to 10), aromatic aster (Symphyotrichum oblongifolium, zones 3 to 9) and inland sea oats (Chasmanthium latifolium, zones 3 to 8) define the restorative green retreat by the bungalows.
“We also reduced the amount of lawn in the original design and replaced several areas [including the space shown here], with Leavenworth’s sedge (Carex leavenworthii, zones 6 to 9) as a water-conscious solution,” Yant says.